
CKD ncp
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) affects between 8% and 16% of the population worldwide and is often underrecognized by patients and clinicians. 1 - 4 Defined by a glomerular filtration rate (GFR) of less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m 2, albuminuria of at least 30 mg per 24 hours, or markers of kidney damage (eg, hematuria or structural abnormalities such a.
nursing care plan for hypertension scribd Jonah Walston
Kidney Transplant. Palliative care. Chronic kidney disease (CKD), also referred to as chronic renal failure, is a condition in which the patient's renal function declines until the kidneys are no longer able to perform their function. According to CDC estimates from 2021, approximately 37 million adults in the United States have CKD.

Read in this post the 5 chronic renal failure nursing care plans (NCP). Chronic Renal Failure or
Individuals with chronic kidney disease (CKD), particularly those undergoing maintenance dialysis, are prone to protein-energy wasting (PEW), the latter of which can be ameliorated with different methods of nutrition support. Dietary counseling guided by dietitians is the key for preventing and managing PEW in CKD.

staging chronic kidney disease Disease todaysveterinarypractice Diseases Club Center 2
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) describes abnormal kidney function or structure. It is common and often occurs with other conditions (such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes). Moderate to severe CKD is also associated with an increased risk of acute kidney injury, falls, frailty and mortality..
NCP 9 Nursing care plan on Renal Failure YouTube
1. Managing Decrease in Cardiac Output 2. Promoting Infection Control and Minimizing Risk of Infection 3. Managing Cognitive Symptoms 4. Providing Skin Care and Maintaining Skin Integrity 5. Promoting Oral Health 6. Initiating Health Teachings and Patient Education 7. Reducing Anxiety and Providing Emotional Support 8.

ncp ckd Chronic Kidney Disease Health Sciences
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is a progressive condition that happens when your kidneys are damaged and can no longer process and filter your blood the way they should. This leads to waste and.

Pin on nursing stuff
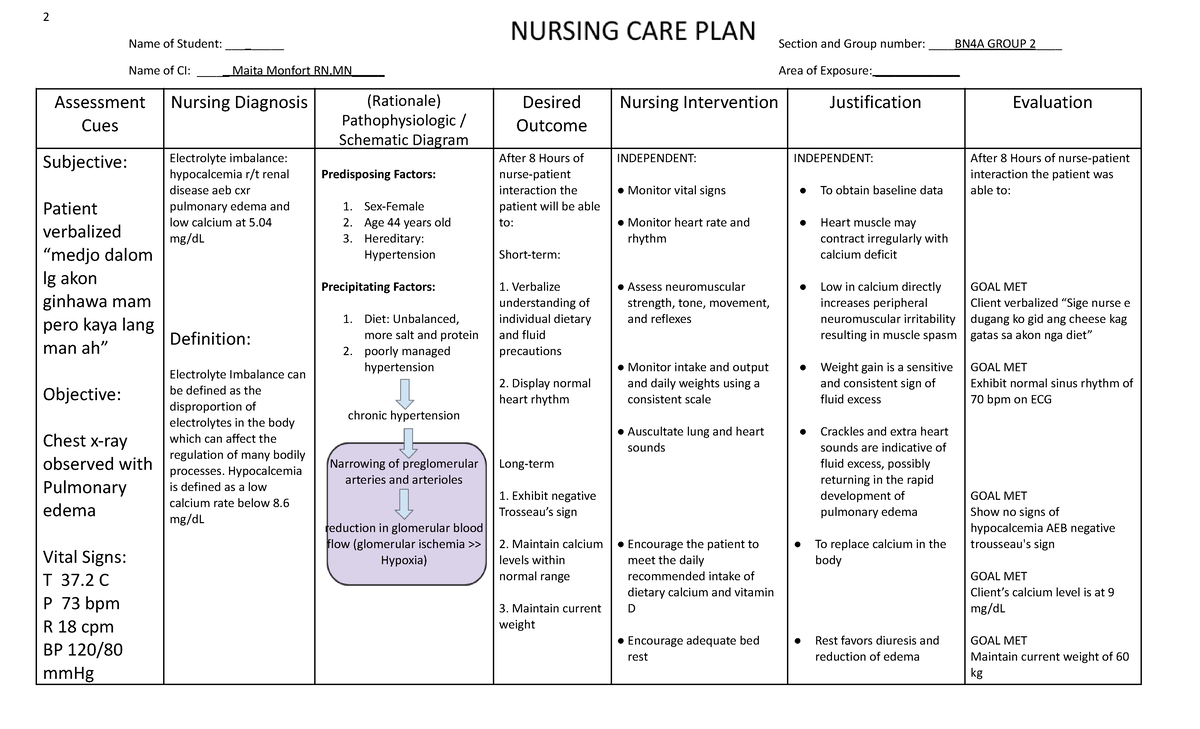
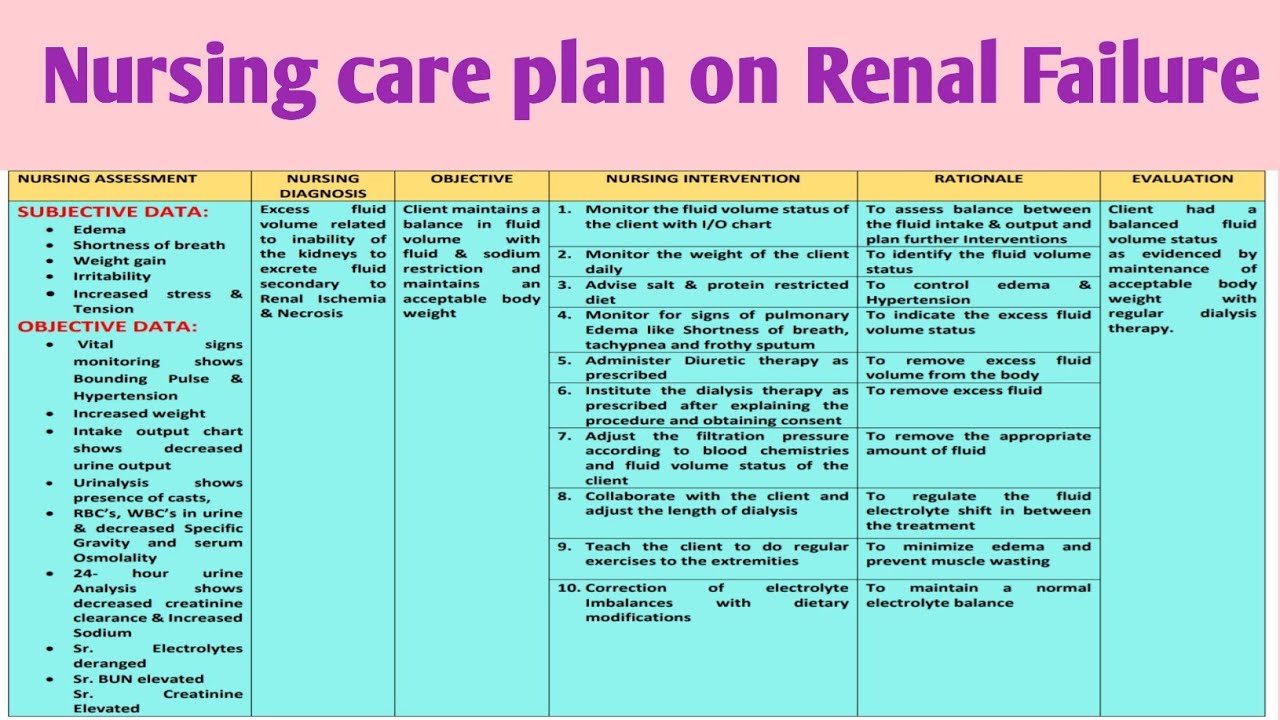
Renal failure is where a patient's kidneys lose the ability to remove toxins and waste from the body. Due to this the body will build up excess levels of potassium, calcium, phosphate, creatinine, urea, and anemia. This can be deadly to a patient if these excess levels are not removed.
NCP Grand CASE NURSING CARE PLAN OF CHRONIC KIDNEY DISEASE PROBLEM NURSING DIAGNOSIS GOAL
Nursing Care Plan. Monitor vitals and the weight of the patient. Monitor the nutritional status of the patient. Advice/counsel the patient to reduce fluid intake significantly. Activity intolerance should be tackled by assessing contributory factors. Accumulation of accessive fluid causes discomfort, therefore assist the patient accordingly to.

Nursing Care Plan CKD PDF Anemia Kidney
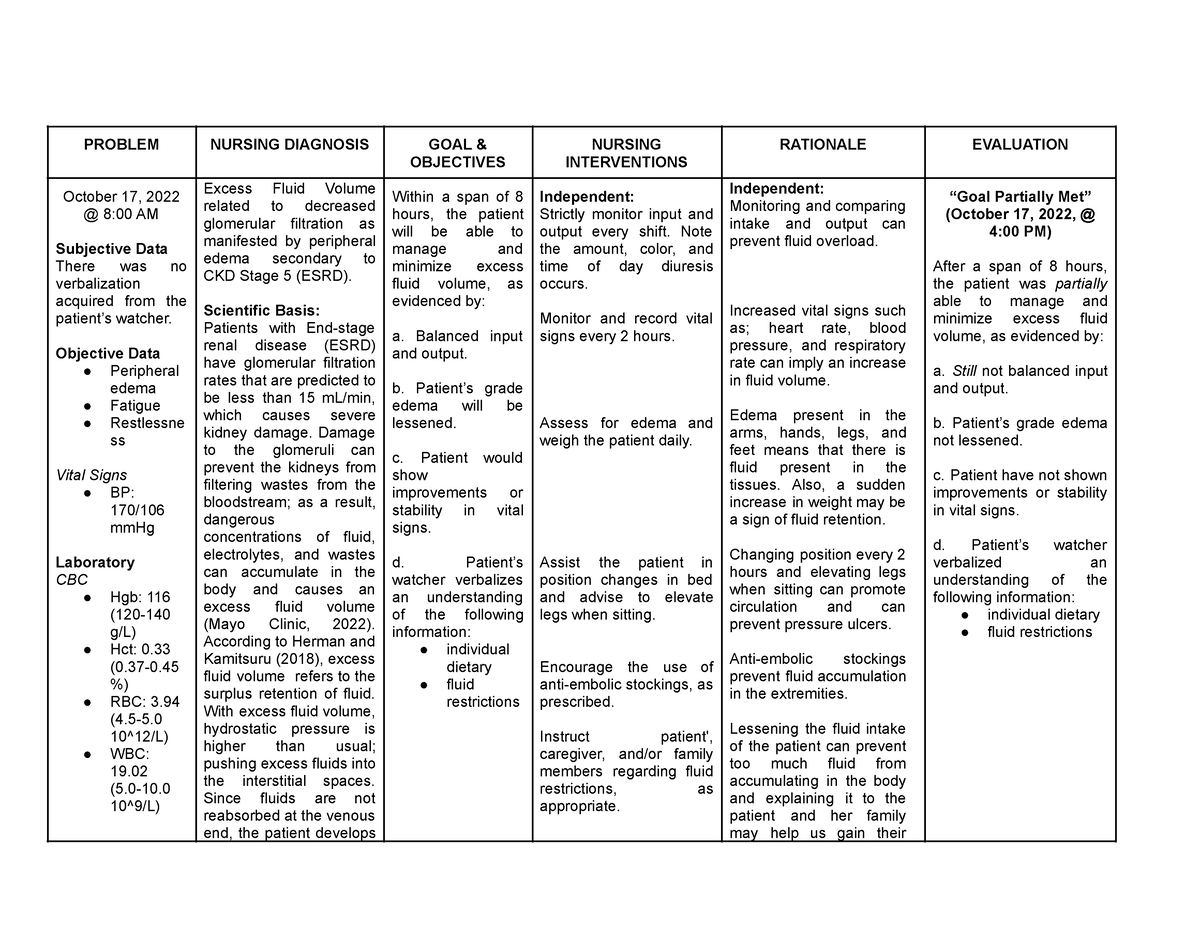
Chronic kidney disease is characterized by a progressive decline in renal function over an extended period, leading to the gradual inability of the kidneys to effectively filter waste products from the blood. Formation of Scar Tissue (Fibrosis):

NCP Format 3 (CKD Chronic Kidney Disease DM Diabetes Mellitus Nephropathy) Enfermedad renal
Chronic kidney disease can progress to end-stage kidney failure, which is fatal without artificial filtering (dialysis) or a kidney transplant. How kidneys work. Show transcript for video How kidneys work. One of the important jobs of the kidneys is to clean the blood. As blood moves through the body, it picks up extra fluid, chemicals and waste.

Chronic Kidney Disease Obgyn Key
Chronic kidney disease is divided into five stages based on the eGFR (estimated glomerular filtration rate), a blood test that measures the kidney's filtering ability. Stage 1 presents as an eGFR of 90 ml/min or higher. This is considered a normal eGFR, and the patient will likely be asymptomatic. Stage 2 CKD is an eGFR of 60-89 ml/min.

Esrd NCP PDF Chronic Kidney Disease Kidney
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) or chronic renal failure (CRF) is characterized by a progressive and irreversible loss of kidney function. Since the kidneys are highly adaptive organs, kidney disease is often not identified until there is a considerable loss of nephrons.

Chronic Kidney Disease Chronic Kidney Disease JAMA JAMA Network
Your doctor may also recommend a water pill (diuretic) and a low-salt diet. Medications to relieve swelling. People with chronic kidney disease often retain fluids. This can lead to swelling in the legs as well as high blood pressure. Medications called diuretics can help maintain the balance of fluids in your body.

Acute Renal Failure Nursing Care Plan And Management Nursing Care Plan Images and Photos finder
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) is defined as the presence of kidney damage or an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) less than 60 ml/min/1.73 mt2, persisting for 3 months or more, irrespective of the cause.[1]

NCP for Nephrotic Syndrome Edema Kidney Free 30day Trial Scribd
When the patient has sustained enough kidney damage to require renal replacement therapy on a permanent basis, the patient has moved into the fifth or final stage of CKD, also referred to as chronic renal failure. Chronic renal failure (CRF) is the end result of a gradual, progressive loss of kidney function.

Chronic kidney disease Trust Hospitals, Kakinada
In nursing, the term chronic kidney disease (CKD) refers to progressive, irreversible kidney damage or a decrease in the glomerular filtration rate (GFR) that lasts for three months or longer. CKD is linked to lower quality of life, higher healthcare costs, and premature death.